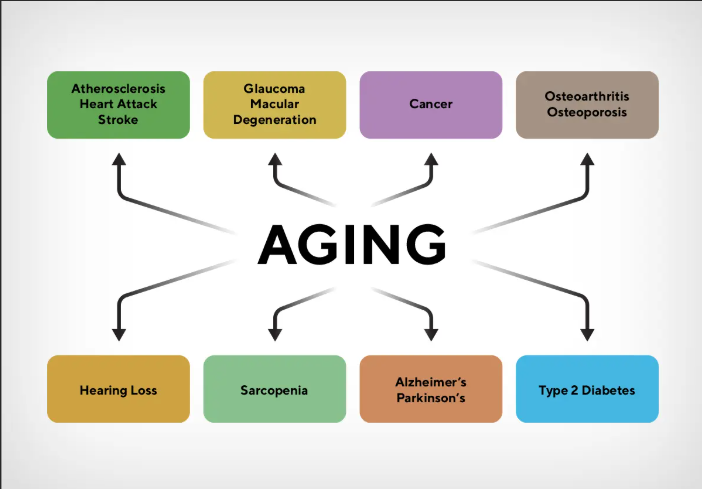
As we age, our bodies undergo a lot of natural changes that can increase or decrease our risk of developing age-related diseases. While some age-related changes are inevitable, there are many steps we can take to reduce our risk of developing diseases like Alzheimer’s, osteoporosis, and heart diseases.
In this blog we’ll talk about the most common age-related diseases, their risk factors and most importantly, provide you with a comprehensive list of how to prevent them.
Table of Contents
Most Common Age-related Diseases:
- Alzheimer’s Disease: A neurological disorder that affects memory, thinking and behavior.
- Osteoporosis: A condition differentiated by brittle and porous bones, increasing the risk of fractures.
- Heart Diseases: A condition in which the heart becomes weak, leading to problems with blood flow and oxygen supply.
- Diabetes: A condition in which body becomes unable to regulate blood sugar levels.
- Cancer: A group of diseases grouped by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells.
Let’s learn about these diseases in brief……..
Alzheimer’s Disease:
Alzheimer’s disease is neurological disorder that affects memory, thinking, and behavior. It is the most common form of dementia, accounting for 60-80% of dementia cases.
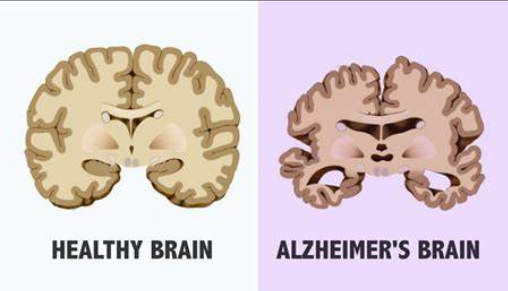
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Genetics: Family history and genetic predisposition can increase the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
- Age: Alzheimer’s disease is a condition that affects older adults with most cases occurring after the age of 65.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, lack of exercise, and social isolation can increase the risk of developing this condition.
Symptoms:
- Memory loss: forgetting things which are recent or new information, recalling familiar words and names.
- Communication and Language: Difficulty with verbal or nonverbal communication, including reading, writing, and comprehension.
- Problem solving and Judgement: Difficulty with normal thinking, making decisions, and judging time and spaces and Mood swings.
Stages:
- Early Stage: Symptoms are mild and may not be noticeable to others.
- Moderate Stage: Symptoms worsen, and daily life becomes more difficult.
- Late Stage: Symptoms are severe and requires full-time care.
Osteoporosis:
Osteoporosis is a condition differentiated by Brittle and porous bones, increases the risk of fractures. It is a condition that affects older adults, especially Women.
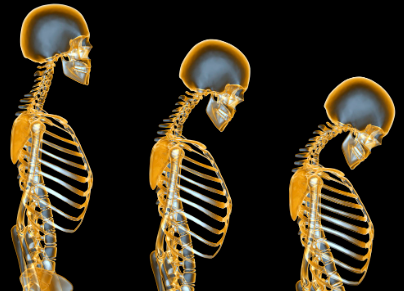
Causes and Risk Factor:
- Genetics: Family history and genetics can increase the risk of developing osteoporosis.
- Hormonal Changes: Decreases in estrogen levels during Menopause can lead to bone loss.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, lack of exercise, and smoking can increase the risk of developing this condition.
Symptoms:
- Back pain: Fractures in the spine can cause pain in back.
- Loss of Height: Vertebral fractures can cause a loss of height.
- Fractures: Osteoporosis increases the risk of fractures, particularly in hips, wrists and spine.
Stages:
- Osteopenia: Bone density becomes lower than normal, but not low enough to be classified as osteoporosis.
- Osteoporosis: Bone density is significantly lower than normal, increasing the risk of fractures.
- Severe Osteoporosis: Bone density is extremely low, and the risk of fractures is high.
Heart Disease:
Heart disease is a condition where the heart becomes damaged, leading to problem with blood flow and oxygen supply. It is the leading cause of death worldwide.
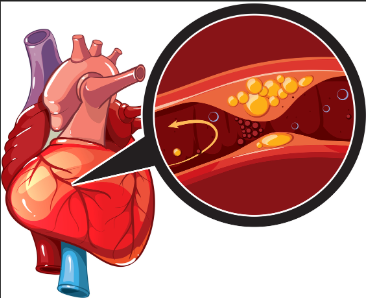
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Genetics: Family history and genetics can increase the risk of developing heart diseases.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of developing heart disease.
- High blood Pressure: Uncontrolled high blood pressure can damage the heart and increase the risk of heart disease.
Symptoms:
- Chest pain: Pain or discomfort in the chest, arms, neck, jaw or back.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing or feeling dizzy even when sitting still.
- Fatigue: Feeling weak, tired, or lacking energy.
- Swelling: Swelling in the legs, ankles or feet.
Stages:
- Atherosclerosis: The buildup of plaque in the arteries, which leads to heart disease
- Heart Failure: The heart becomes unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s requirements.
- Coronary Artery Disease: The coronary arteries become narrow and blocked, reducing blood flow to the heart.
Diabetes:
Diabetes is a condition where the body becomes unable to regulate blood sugar levels. It is a leading cause of death and disability worldwide.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Genetics: Family history and genetics can increase the risk of developing diabetes.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor Diet, lack of exercise, and obesity can increase the risk of developing diabetes.
- Insulin Resistance: The body becomes resistant to insulin, making it harder for glucose to enter the cells.
Symptoms:
- Increased Thirst and urination: When there is too much glucose in the blood, the body tries to flush it out by producing more urine.
- Fatigue: High blood sugar levels can cause fatigue, weakness, and lack of energy.
- Blurred Vision: High blood sugar levels can cause the lens in eye to swell, leading to blurred vision.
- Slow healing of Cuts and Wounds: High blood sugar levels can affect the body’s ability to heal wounds.
Stages:
- Prediabetes: Blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to classified as diabetes.
- Type 1 diabetes: The body’s immune system attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin, resulting in a complete deficiency of insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes: The body becomes resistant to insulin, making it harder for glucose to enter the cells, and the pancreas is unable to produce enough insulin to meet the body needs.
Cancer:
Cancer is a group of diseases characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells. it is a leading cause of death worldwide.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Genetics: Family history and genetics can increase the risk of developing cancer.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of developing cancer.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to Radiation, chemicals and other environmental toxins can increase the risk of developing cancer.
Symptoms:
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Losing weight without trying, particularly if its significant.
- Fatigue: Feeling weak, tired or lacking energy.
- Pain: Persistent pain or discomfort that lasts for weeks or months.
- Changes in Skin: New moles, sores, or changes in the size or color existing moles.
Stages:
- Stage 1: Cancer is limited to the place where it started and hasn’t spread to other parts of the body.
- Stage 2: Cancer has grown, but it hasn’t spread to distant parts of the body.
- Stage 3: Cancer has spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes.
- Stage 4: Cancer has spread to distant parts of the body.
Prevention Strategies:
- Don’t Smoke: Smoking is a leading cause of Most of diseases mostly Cancer.
- Eat healthy diet: Focus on consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in moderate-intensity exercise, such as walking, cycling, or swimming for at least 30 minutes per day.
- Limit Sun Exposure: Protect your skin from the sun by seeking shade, wearing protective clothing, and applying sunscreen.
- Get Vaccinated: Certain vaccines, such as the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine, can help prevent certain diseases.
Conclusion:
Preventing age-related diseases requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates healthy lifestyle choices, stress management, and social connection. By understanding the causes, risk factors, symptoms, and stages of these diseases, we can take proactive steps to reduce our risk and promote overall health and well-being.
Read my other blog on Healthy recipes to Avoid this diseases.
Follow us on